CHAPTER II - DETAILED DESCRIPTION
SECTION I DESCRIPTION OF THE COMPONENT
PARTS OF THE REFRIGERATION SYSTEM
1 - Compressor And Motor Assembly
2 - Condenser
Air Cooled
Water Cooled
3 - Strainer - Refrigerant
4 - Capillory Tube
5 - Evaporator Coil
6 - Accumulator
7 - Thermostat
SECTION II DESCRIPTION OF CABINET REMOVAL
1 - Cooling Unit
Tank Type Cooler Assembly
Coil-on-Coil Cooler Assembly
Shell Type Cooler Assembly
2 - Drain or Precooler
3 - Water Regulating Valve
SECTION III DESCRIPTION OF CABINET REMOVAL
1 - Full Wrap-Around Cabinet
2 - Wrap-Around With Front Panel Removable
3 - Panel Type Cabinet
4 - Wall Hung And Semi-Recessed Models
SECTION I - DESCRIPTION OF THE COMPONENT PARTS OF THE REFRIGERATION SYSTEM
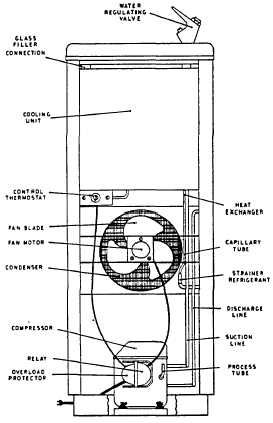
FRONT VIEW
The refrigeration system and related component parts
consist of the following:
1 - Compressor and Motor Assembly
2 - Condenser: Air Cooled
Water Cooled
3 - Strainer - Refrigerant
4 - Capillary Tube
5 - Evaporator Coil
6 - Accumulator
7 - Thermostat
1.
COMPRESSOR AND MOTOR ASSEMBLY
The compressor and motor assembly is located in the
machine compartment of the water cooler. The
assembly is suspended on springs, inside an all welded
steel housing and is lubricated by a wax-free dehydrated
oil. The compressor assembly is provided with an
external electrical terminal enclosure, located on the side
of the housing.
The electrical terminal enclosure has a high
impact, fire resistant cover. The relay and overload are
mounted in this enclosure.
When supplied, the relay operates in the starting
of the compressor motor and disconnects the starting
winding when the motor reaches its proper speed
The overload protector, retained against the
compressor housing, is of the automatic reset type and
breaks the circuit within a few seconds if the compressor
fails to start. The circuit will also be interrupted if the
compressor overheats during operation.
'When required a capacitor is used on some water
coolers to increase the starting torque of the compressor
motor and/or aid its operation.
2.
CONDENSER
As the refrigerant passes through the condenser, heat is
removed, causing the refrigerant to cool and condense
to a high pressure liquid. The principle means of
removing heat is by natural or forced convection air or
water.
(a)
Air-Cooled Condenser - The static condenser
depends upon its large exposed surface area and
natural convection air in a favorable
5