CHAPTER VI - MISCELLANEOUS COOLERS
SECTION I COMPARTMENT WATER COOLERS
1 - Explanation of the Bottle -
Comportment Refrigeration System
2 - Explanation of the Pressure-
Comportment Refrigeration System
3 - Maintenance
4 - Service and Trouble Shooting
SECTION II
EXPLOSION PROOF WATER COOLERS
SECTION III
BELT DRIVEN OR OPEN TYPE
REFRIGERATION SYSTEM WATER
COOLERS
1 - Explanation
2 - Maintenance
SECTION I - COMPARTMENT WATER COOLERS
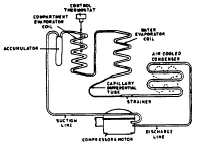
SCHEMATIC -REFRIGERATION
COMPARTMENT-BOTTLE WATER COOLER
1.
EXPLANATION OF THE BOTTLE -
COMPARTMENT REFRIGERATION SYSTEM
The high pressure liquid refrigerant passes through the
capillary tube to the water evaporator. Upon leaving the
water evaporator, it travels through a weight check
valve, which prevents freezing of the water system, to
the compartment evaporator. After circulating through
the compartment coil, the refrigerant then passes
through the accumulator and back to the compressor.
The system is controlled by one thermostat whose
power element is strategically located on the side of the
compartment evaporator. When the water demands
more cooling, the warmer refrigerant vapor passes from
the water evaporator through the weight check valve to
the compartment evaporator. This in turn warms the
power
element
of
the
thermostat
causing
the
compressor to start, regardless of the temperature of the
compartment. The compressor will also start when the
compartment
requests
cooling
and
the
water
temperature is correct.
2.
EXPLANATION OF THE PRESSURE -
COMPARTMENT REFRIGERATION SYSTEM
Early designs of the compartment, pressure water
system use a solenoid valve in the water evaporator
outlet controlled by a thermostat to prevent freezing of
the water cooling system. A capillary tube branching
from a specific turn of the water evaporator supplies
refrigerant for cooling of the compartment evaporator.
When the water requires more cooling, the thermostat
contacts close causing
the solenoid valve to open and the compressor to start.
When the compartment only requires more cooling, its
thermostat contacts close causing the compressor to
start.
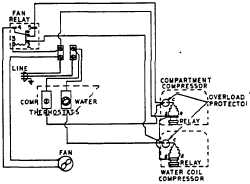
Later models use two refrigeration systems,
each operating independently of one another. Each
system has its own controlling thermostat to operate and
control its system.
Both refrigeration systems share a common air
cooled double circuited condenser and use one fan.
A relay is employed to actuate the fan when
either system starts.
WIRING DIAGRAM FOR COMPARTMENT
PRESSURE WATER COOLER
3.
MAINTENANCE
An occasional defrosting of the compartment evaporator
is the only difference for general maintenance of the
cooler. When defrosting of the compartment is required,
disconnect electrical power supply. Remove ice cube
trays and place a pan of hot water in the compartment.
The door can remain open. Defrosting requires about 15
minutes depending upon the frost build-up. When
completed, fill the ice trays with fresh water and connect
the electrical supply.
4.
SERVICING AND TROUBLE SHOOTING
When trouble is encountered with the compartment
water coolers, service procedures mentioned earlier in
this manual should be followed.
15