VARIMOT® INFORMATION
GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS
Each drive Is tested before it leaves the factory. Proper
installation and operation are essential for good performance.
The drive must be fastened on a solid base, free of vibration
and according to the mounting position indicated on the
nameplate. Feet or flanges can be damaged if the unit is not
mounted on a solid and even mounting base. Shim, if
necessary.
Do not hammer on sprockets, couplings, etc. when mounting
these items on the output shalf. Severe damage can be done
to the bearings.
The shaft diameters have tolerances of +.000"-.0005" for
diameters smaller than 1.500", and + .000"-.001" for
diameters
larger than 1.500". Tolerances for metric shafts are listed in
Eurodrive's catalogs.
Each Varimot is equipped with a friction disc (driven disc) and
a driving disc. Varimots D12, D22, D32, and D42 have a
friction disc from a phenolic material.
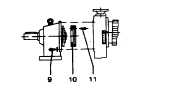
REPLACEMENT OF A PHENOLIC FRICTION DISC:
Remove four (4) bolts - #9
Split the traction housings
Mark the friction disc/hollow shaft assembly so the lobe
cams at the end of the shaft assembly can later be
engaged at the same place
Remove the friction ring screws - #11
Replace the friction disc - #10
Before assembling the housing, clean the driving disc
face so it is completely free from oil and grease
On Varimot models D23, D33 and D43, the friction disc
cannot be separated from the hollow shaft assembly because
the carbon disc is an integral part of the shaft assembly.
When the friction disc is checked or replaced, perform the
following regreasing of the bearings and lobe cams:
1.
Pull out hollow shaft assembly - #3
2.
Regrease needle bearings - #7 (Shell Alvania R3 or
equivalent)
3.
Grease lobe cams - #8 (Lubriplate Grease GR-132)
When regreasing, do not overfill cavity. Too much grease
generates an excess amount of heat.
If the lobe cams are worn excessively and can't function
properly by sliding over each other, replace both shafts
involved.
ASSEMBLING THE TRACTION HOUSING
1.
When assembling the unit, make sure the cams are
engaging the same way as they came out.
2.
The cams must be properly engaged. Push the shaft
assembly "in" against the spring force.
3.
Tighten bolts #9 diagonally making sure that the
cams are properly engaged.
Upon completion of the assembly, run the Varimot, under
power, through the whole speed range checking for noise or
vibration.
If due to operation problems, (jamming of the driven machine)
the friction disc has stalled-out and the disc is damaged or
has become noisy: Remove the hollow shaft assembly with
friction disc completely. Face off the friction disc on a lathe.
Remove enough material to clean up the face. Reinstall the
shaft assembly.
REMOVAL OF THE DRIVING CONE
The driving cone can be removed in 2 ways:
1.
By using a wheelpuller
2.
Pressing the rotor out of the driving cone.
When method 1 is used make sure the fingers of the puller
don't fracture the cast iron driving cone. Use a spacer
between the puller fingers and the driving cone. This will
reduce the possibility of fractures.
Method 2 requires complete disassembly of the motor.
1.
Remove the fan guard, enshield and stator.
2.
Remove the snapring which holds the bearing behind
the driving cone in its' place.
3.
Press out the rotor shaft.
For assembly of the unit:
1.
Install rotor shaft with bearing.
2.
Install snapring.
3.
Press on the driving cone.
4.
Assemble stator, end shields, fan guard.
VARIMOT® UNITS SUITABLE FOR OUTDOOR DUTY OR
WASHDOWN APPLICATIONS
The units are equipped with drain hoes at the lowest point for
the mounting position listed on the nameplate.
If the mounting position gets changed, please make sure new
drain holes are drilled so the water or condensation can drain
off properly.
Options:
Varimots can be supplied with (See Diagram):
Electric remote control motor - 23C0460V,3 Phase, or 115V,
Single Phase
Remote
speed
indicator
(percentage
speed
indicator,
20100%)
Handwheel with speed position indicator (HS Option). HS
Option can only operate with the handwheel shaft horizontal.
The torque is transmitted from the driving disc to the friction
disc. Torque demand at the output shaft is transformed into
axial load against the driving disc through a set of cams called
the "torque compensator." By that means, wear is avoided at
no load.
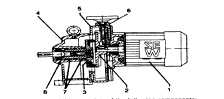
This
variable
speed
drive
consists
of
the
following
components:
1)
Motor with dove tail slide
2)
Driving disc
3)
Hollow shaft with friction ring and output shaft
4)
Housing
5)
Traction housing
6)
Speed adjustment
7)
Needle bearings
8)
Torque compensator (lobe cams)
9