TM 10-4320-317-13
(1) Divide the horizontal base of the triangle into spaces on the same uniform scale used to divide the base of the
ground profile graph. Mark off spaces along the triangle base to at least 39,000 ft (11,895 m).
(2) Divide the vertical, left-hand edge of the triangle into spaces on the same uniform scale used to represent
elevation changes on the ground profile. Mark off spaces along the vertical side of the triangle as follows:
(a) Zero represents the elevation of the pumping station.
(b) The upper left-hand comer represents 300 ft (91.5 m) above the pumping station.
(c) The lower left-hand comer represents 600 ft (183 m) below the pumping station.
(3) Draw a straight, diagonal line from the 300 ft (91.5 m) mark on the vertical scale to the 39,000 ft (11,895 m)
mark on the horizontal scale. This line will form the hypotenuse or long side of the triangle.
(4) Making sure all lines have a straight edge, cut the triangle along the three sides drawn (horizontal, vertical, and
diagonal).
i.
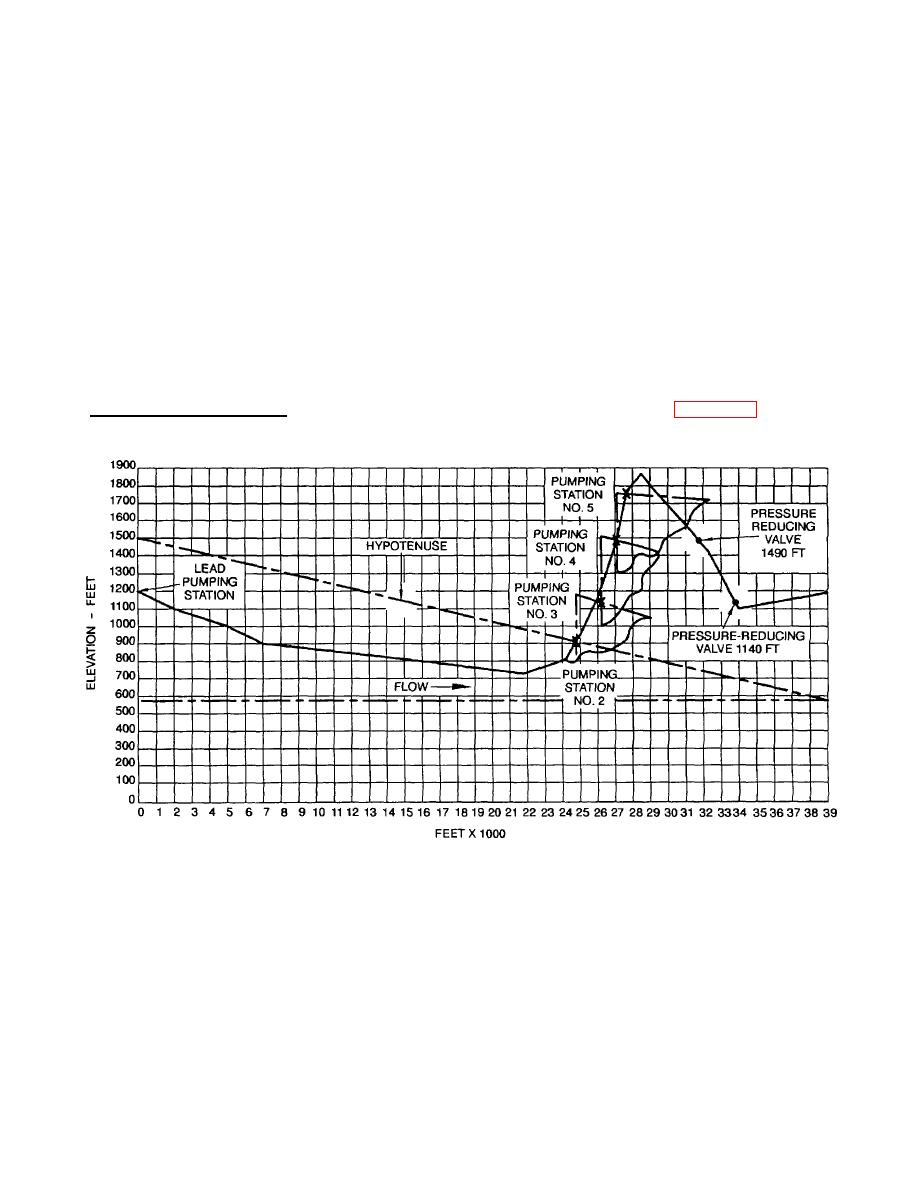
First Boost Pumping Station. Using the ground profile and pump spacing triangle (Figure 2-4), determine the
location of the first boost pumping station as follows:
Figure 2-4. Ground Profile and Pump Spacing Triangle
(1) Place the pump spacing triangle on the ground profile.
(2) Align the vertical side of the pump spacing triangle with the vertical (elevation) side of the ground profile, so
that the zero mark of the spacing triangle is on the lead pumping station mark of the ground profile.
2-23


