TM 10-4320-317-13
(3) Make sure the horizontal side of the spacing triangle is exactly parallel with the horizontal base of the ground
profile. Horizontal spacing marks on both the pump spacing triangle and ground profile should be exactly aligned.
(4) Mark the point at which the hypotenuse (or long side of the spacing triangle) crosses the ground profile. This
will be the location of the first boost pumping station.
NOTE
If level of ground profile is below base of pump spacing triangle, extend
the line of the spacing triangle hypotenuse until it crosses the ground
profile.
j.
Second Boost Pumping Station. To determine the location of the second boost pumping station, place the zero
mark of the spacing triangle on the first boost pumping station mark of the ground profile. Mark the point at which
the spacing triangle hypotenuse crosses the ground profile. This will be the location of the second boost pumping
station. Locations of successive boost pumping stations are determined in the same way.
K.
Elevation Drops. After locations of pumping stations have been plotted, check ground profile for any sharp declines
in elevation along hoseline route. An excessive drop in elevation will significantly increase the pressure of water
as it flows downhill. If pressure builds to 225 psig (155 kPa), hoseline can rupture and equipment failure will result.
Therefore, when the ground profile indicates a sharp elevation drop along the route, a pressure-reducing valve
must be installed in the hoseline.
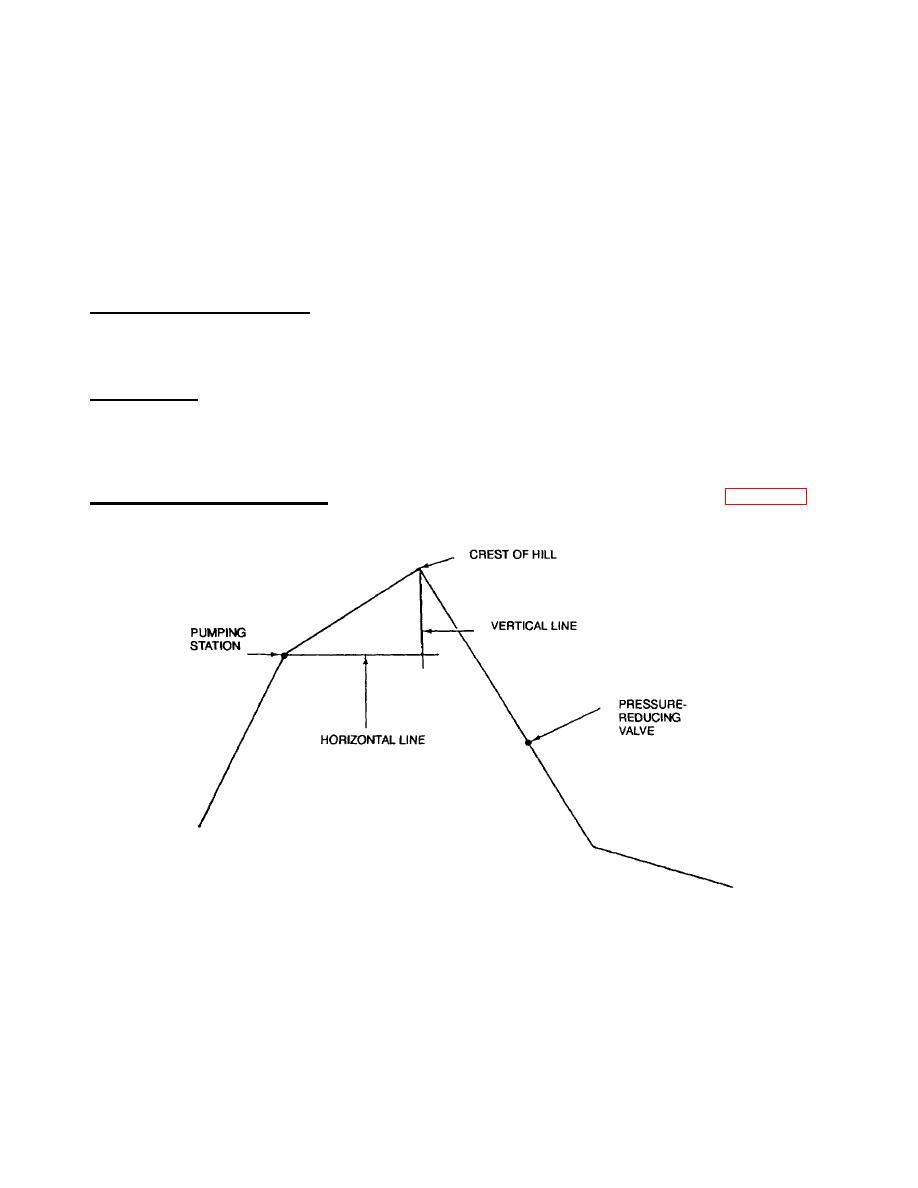
I.
Pressure-Reducing Valve Location. To determine the location of the pressure-reducing valve (Figure 2-5), refer to
the ground profile and proceed as follows:
Figure 2-5. Pressure- Reducing Valve Location
2-24


